The Insight Hub
Explore the latest news and insights across various topics.
Fair Contracts or Just Smart Tricks? Unraveling the Mystery of Smart Contract Fairness
Discover the truth about smart contracts: Are they fair agreements or just clever tricks? Uncover the mystery today!
Exploring the Fine Line: Are Smart Contracts Truly Fair?
As we delve into the realm of blockchain technology, the concept of smart contracts emerges as a revolutionary component, promising to streamline transactions and enhance transparency. However, the question arises: are these contracts truly fair? Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, allowing for automation without the need for intermediaries. While this eliminates human error and potential bias, it also raises concerns about the inherent fairness of the algorithms that govern these contracts. If the underlying code is flawed or biased, the contract itself may perpetuate existing inequalities rather than alleviate them.
Moreover, the accessibility of smart contracts and the knowledge required to navigate them play a crucial role in determining their fairness. Many individuals may lack the technical expertise to fully understand or audit these contracts, leading to a disparity between those who can leverage this technology and those who cannot. In light of these considerations, it becomes essential to address the ethical implications of smart contracts as we continue to innovate. Establishing guidelines and regulations to ensure that smart contracts are accessible, transparent, and free from bias is vital for fostering a more equitable digital future.
Counter-Strike is a popular series of first-person shooter games that emphasize team-based gameplay and strategy. Players can choose to join either the terrorist or counter-terrorist side, engaging in various scenarios. For those looking for perks while playing, check out the bc.game promo code to enhance your gaming experience.
Smart Contracts Unveiled: Essential Features for Fairness
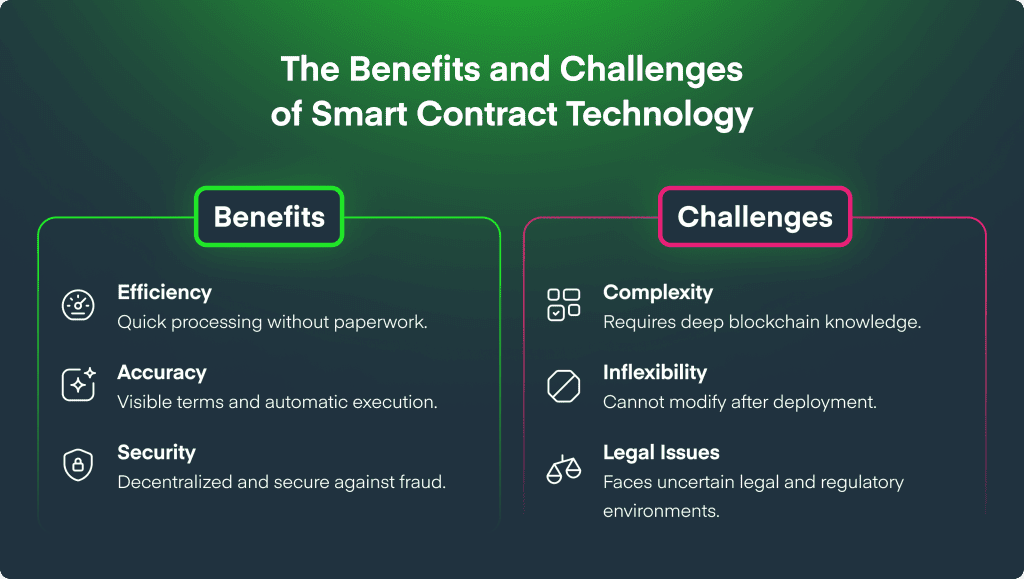
Smart contracts have emerged as a revolutionary technology, enabling automated transactions without the need for intermediaries. One of their essential features is transparency, which allows all parties involved to access the same information, ensuring that every aspect of the contract's execution can be verified. This transparency fosters trust among users, as they can be confident that the conditions set within the contract will be adhered to without manipulation. Furthermore, smart contracts can be stored on a decentralized blockchain, which enhances their security and resistance to fraud.
Another critical aspect of smart contracts is their immutability. Once a smart contract is deployed on the blockchain, its code cannot be altered, ensuring that the terms agreed upon by the parties remain intact. This characteristic is vital in maintaining fairness, as it protects all involved parties from potential disputes regarding contract modifications. Additionally, smart contracts can be programmed with complex logic, allowing them to execute various functions automatically, such as releasing payments when specific conditions are met, further enhancing their utility in ensuring equitable outcomes.
Do Smart Contracts Eliminate Unfair Practices? A Closer Look
Smart contracts have emerged as a revolutionary technology capable of transforming various industries by automating and enforcing agreements without the need for intermediaries. By utilizing blockchain technology, these contracts ensure a transparent and tamper-proof environment where all parties involved can trust the terms outlined in the code. As a result, unfair practices such as fraud, manipulation, and non-compliance could be significantly reduced. Their inherent qualities allow for real-time execution and monitoring, providing stakeholders with an immutable record of all transactions, which can dissuade unethical behaviors that are often prevalent in traditional contract systems.
However, while smart contracts offer numerous benefits, they are not a one-size-fits-all solution to eliminating unfair practices. Issues such as coding errors, ambiguous terms, and lack of legal recognition can lead to unintended consequences. Moreover, the ethical implications of completely automated systems prompt important discussions about accountability and decision-making. Thus, while smart contracts may substantially mitigate the risk of unfair practices, they are best employed as part of a broader framework that combines technology with robust legal standards and human oversight to ensure fairness and justice in transactions.